
Results
Phase III 2024
Phase name: Validation of SH-SAW sensor-based detection method.
Phase results:
The research carried out at this stage focused on the determination of glyphosate from real water samples (collected from the Drăgășani dam area - Olt River), selectivity studies, and the dissemination of the obtained results. Special attention was paid to the results correlation of the two methods (UHPLC-MS/MS and MIP-SAW) of glyphosate detection.
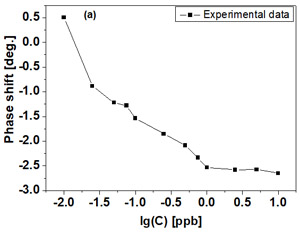
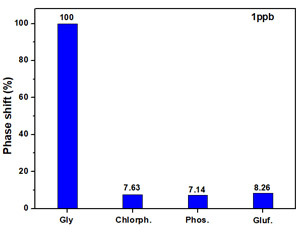
The detection of Gly in real samples (collected from the area of the Drăgășani dam - Olt River) was carried out at concentrations in the range of 0.01-50 ppb. The response of the MIP-SAW sensor to these concentrations is illustrated in Figure 1.a. A linear range in the 0.025-1 ppb concentration range was observed for the MIP-SAW sensor tested in real samples, and the obtained sensitivity was approx. 0.99 deg./ppb. Chlorpyrifos, phosmet, and glufosinate were used as interferents in carrying out the selectivity tests. In Figure 1.b the MIP-SAW sensor shows a high value of the phase shift in the presence of Gly for the concentration of 1 ppb compared to the value obtained for the other interfering species, demonstrating the high selectivity of the developed sensors.
(a) (b)
Figure 1. (a) Response of the MIP-SAW sensor to different concentrations of Gly from real samples and (b) Selectivity of the MIP-SAW sensor to different interferents.
The validation of the method proposed in this project (based on MIP-SAW sensors) was achieved by comparing the obtained results with the standard UHPLC-MS/MS method for determining glyphosate from water samples. The experimental results demonstrated that the developed MIP-SAW sensors can be successfully used for very low concentrations of glyphosate from real samples.
Deliverables:
• Report on standard UHPLC-MS/MS method measurements of Gly concentration in collected surface water sample.s
• Report on MIP-SAW sensor measurements of water samples.
• Report on methods validation.
• Periodical progress reports.
•
Publication of 2 scientific papers in ISI journals (Q1 or Q2).
Phase II 2023
Phase name: Device functionalization and morphological characterization of polymeric materials with antibody abilities. Development and optimization of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantitative determination of glyphosate in surface water samples. SAW sensor testing. Validation of detection method based on SH-SAW sensors
Phase results:
During this phase, molecular printing (chitosan -based) activities of the detection area of the SAW device (Figure 1) and the morphological and electrochemical characterization of the printed layers were carried out.
Figure 1. Optical image of the encapsulated MIP-SAW sensor
Electrical measurements (using standard solutions of GLY) were performed for the SAW devices both before and after their functionalization. Slight phase variations of about 1.3°/minute were obtained for non-functionalized devices (behavior due to the wetting phenomenon of the detection area) and variations of about 6°/minute for the MIP-SAW sensors for 1 ppb glyphosate concentration.
Another direction addressed within this phase was the optimization and validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the direct analysis of polar pesticides (GLY, AMPA, glufosinate, amitrol, 1,2,4-triazole, ethephon, cyanuric acid) in water samples, without derivatization, using a porous graphitic carbon column. The analysis method was used to determine the content of polar pesticides in the surface waters collected from the middle and lower basin of the Olt River. A case study was carried out to allow a detailed assessment of the contamination of surface waters taken from the middle and lower reaches of the Olt River by investigating different classes of pesticides (organophosphates, organophosphorus, triazines, carbamates, acid herbicides and polar pesticides), with the identification of several point sources of contamination. The identified compounds come mainly from municipal wastewater treatment plants, but also as a result of agricultural and industrial activities. GLY and its metabolite, AMPA were not detected in surface waters of the study area, except for one point location where the AMPA metabolite was detected. As a result, for the next sampling session, the expansion of the study area will be taken into account, by including some rivers and streams located in the immediate vicinity of agricultural areas, and also the sampling period will be correlated with the time of pesticide application in agriculture and the presence of precipitation that facilitates the transfer of pesticides from the surface of agricultural land to surface water.
Deliverables:
• Report on the functionalization process of SAW devices
• Report on the morphological and electrochemical characterization of the MIP-SAW sensor
• Report on optimized parameters for the UHPLC-MS/MS method used for GLY detection
• Report on the optimized sample extraction protocol
• Report on the analytical performance of the UHPLC-MS/MS method for the detection of GLY.
• Report on the standard preparation protocol of glyphosate solutions
• Report on the response characteristics of SAW and MIP-SAW sensors
• Report on the water sample collection protocol
Phase I 2022:
Phase name: Fabrication of the SAW device based on horizontal guided shear waves. Functionalization of manufactured devices. Definition of the development process of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantitative determination of glyphosate
Phase results:
In the current phase, the SH-SAW structures based on the delay line configuration were designed using the dedicated CleWin software tool. The center frequency of the designed devices is about 121 MHz for the selected substrate (B-LiTaO3) and orientation. The three photolithographic masks were manufactured using the DWL 66fs Laser Lithography System equipment, available at IMT-Bucharest.
Another important activity carried out in this research consisted in the fabrication of SH-SAW devices on B-LiTaO3 substrate. The interdigitated transducers and the detection area were fabricated of Cr/Au, and the guide layer used in our application was fabricated of a SiO2 layer, with a thickness of about 3 μm. Finally, the fabricated devices were optically investigated and encapsulated.
Another activity carried out during the first stage was the preliminary functionalization test for SH-SAW devices. The molecular imprinting of chitosan with glyphosate on Au substrate was obtained by the electrochemical deposition technique (Figure. 1).
The development process of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of GLY, AMPA and GLU in water samples was also started. After optimizing the amount of derivatization reagents (Figure 2), so that calibration performance can be achieved, the limit of detection (LD), limit of quantification (LQ) and percent recovery will be estimated for each individual analyte.
Since typical C18 reversed-phase columns do not have satisfactory retention efficiency due to the charge that polar pesticides possess in the aqueous phase, for the optimization and subsequent validation of the HPLC-MS/MS method (for the determination of polar pesticides), the use of anion exchange chromatographic columns for the retention and separation of analytes on the column, followed by detection by UHPLC-MS/MS will be considered.
Deliverables:
• Report on the design and fabrication of photolithographic masks
• The fabrication process of the SH-SAW devices, on quartz substrate
• Characterization of the developed devices
• Preliminary tests regarding the functionalization process of the devices
• Initial parameters of the UHPLC-MS/MS method used for glyphosate detection
