
Results
Results ()in Romanian
Prezentare succintă a rezultatelor obținute în cadrul proiectului.
Obiectivul central al proiectului SOLARSiC a fost proiectarea, fabricarea si testarea unor fotodetectori pe SiC pentru domeniul UV. In urma optimizarii tehnologiei de fabricare a structurilor de test s-a ajuns la concluzia ca fotodetectorul UV trebuie sa aiba la baza o dioda Schottky (structura verticala) cu un electrod de poarta (anod) transparent (ITO) tratat la o temperatura moderata (400°C) si un contact ohmic (catod) format dintr-un sandwich metalic Ti/Ni tratat la o temperatura ridicata (1050°C, 3 min, atmosfera de Ar). Astfel, raspunsul fotodetectorului UV, respectiv performantele sale electrice sunt semnificativ mai bune dupa aplicarea tratamentelor termice, asigurand pe de o parte o mai buna omogenitate a contactului, iar pe de alta parte un fotoraspuns la lumina UV de 3 ordine de marime si timpi de reactie foarte mici ( <1s). Pentru testarea si validarea in conditii de laborator ale structurilor de test, acestea au fost incapsulate utilizand tehnologia firului de aur, un exemplu fiind prezentat in Fig. 1.
 |
|
|
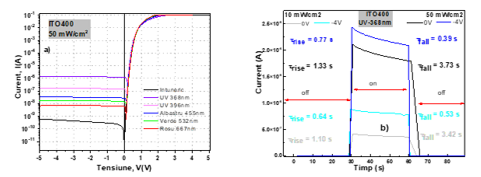
Fotodetectorii au fost testati electric la mai multe lungimi de unda din domeniul UV + vizibil, cu accent pe domeniul UV (368, 396 nm), atat in regim static (caracteristici I-V), cat si in regim dinamic (caracteristici I-t, la V = const.). De asemenea, au fost aplicate doua densitati de putere a intensitatii luminoase (10 mW∕cm2, respectiv 50 mW∕cm2). Performantele fotodetectorilor fabricati pe SiC au fost validate in conditii de laborator prezentand o crestere cu 3 ordine de marime a curentului si un timp de raspuns in regim dinamic mai mic de 1s (Fig. 2).
 |
|
|
______________
Estimated results
- O1. To bring new knowledge related to electrical properties of the novel SiC based PDs.
Evaluation of SD SiC-SBUV PD obtained using transparent (ITO ~ 100 nm) and semitransparent (Ni, Au, Pt < 20 nm) metallic films on SiC.
Evaluation of IDEs/MSM SiC-SBUV PD obtained using a single step photolithography process.
Enhancing the PDs performances using nanoscale metallic plasmonic antennas.
In-depth understanding of the transport mechanisms in novel metallic decorated structures.
Developing a quick characterization technique to classify PD structures as a function of temperature and wavelength ranges.
- O2. To efficiently engineer the SiC based PDs, formed with either metallic ultra-thin films or nanoparticles.
High performance Schottky contacts on SiC using transparent and semitransparent metals.
Design and fabrication of IDEs type structures decorated with metallic NPs or NWs.
Developing a reliable packaging technique for the new SiC PDs.
- O3. To obtain the optimum design and easily reproducible technology for SB PDs based on SiC.
Fabrication of both vertical (SD) and lateral (IDEs/MSM) photodetectors.
Selection and establishment of the optimum architecture and technology for high performance SiC-SBUV PD.
Evaluation of the stability and reliability of the SiC-SBUV PD under realistic operating and processing conditions, and consequently the feasibility of their usage in large-scale technology.

