Welcome to NANODEC website!
Adaptive mobile mixing and dispersing system using nanoparticles into innovative colloidal solutions for chemical, biological and radiological agents’ mitigation
Demonstration experimental project
Project duration: 26 October 2020- 25 October 2022
Project budget: 600.000 RON
Main domain: Information and communication technology, space and security

Results
| Results 2022 | Results 2020- 2021 |
| Rezultate 2022- final (in Romanian) | |
- Development and synthesis of novel solutions, consisting of innovative nanoparticles-enriched formulations, to enhance decontamination efficiency for chemical and biological warfare agents (BCWA). The new decontamination formulations suitable for BCWA comprise an active organic solution, as dispersion media, and three types of nano and microsized adsorbents: ZnO, TiO2 and zeolite, employed for the enhancement of the decontamination performances of the organic solution (higher antimicrobial activity and higher capacity of neutralizing chemical agents).
- The decontamination efficiency was evaluated on two real chemical warfare agents - mustard gas (HD) , soman (GD) and on biological warfare agent Bacillus anthracistrough specific investigation tools: surface monitoring with swabs method, minimum inhibitory (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) evaluations, time-kill tests, for microorganisms and GC-MS for monitoring chemical agents, on different types of surfaces (glass, painted metal, rubber, cotton butyl rubber).
Synthesis of the decontamination solution enriched with nano/micronized adsorbents
The materials employed for the preparation of the decontamination formulations: 2-Ethoxyethanol (≥ 99.8 %, Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether), monoethanolamine (≥ 98 %,), Sodium hydroxide (≥98%,), Isopropyl alcohol (≥99.7%, Sigma Aldrich), Sodium lauryl sulfate (SDS) from Sigma Aldrich), and nano/micro-sized adsorbants ZnO, TiO2 and Zeolite ( clinoptolilete type).
Table 1 summarizes the decontamination formulations obtained.
Table 1. – Nanosized components of the decontamination formulations.
NPs Sample |
Blank (SD)* |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
ZnO (wt.%) |
0 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
TiO2 (wt.%) |
0 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
Zeolite (wt.%) |
0 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
* SD: 2 - Ethoxyethanol, monoethanolamine, sodium hydroxide, isopropyl alcohol, SDS. S1, S2, S3 and S4, contain, besides SD, the corresponding amount of NPs mentioned above.
The morphology of the nano/micro-sized adsorbents used in the decontamination solutions was investigated through SEM analysis and is presented in Figure 1.
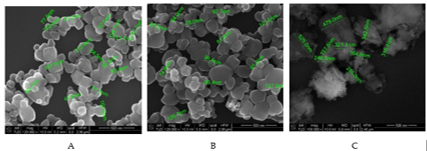 |
Fig. 2. SEM images of the NPs employed in the decontamination solutions: (A) – ZnO NPs; (B) TiO2 NPs; (C) Zeolite NPs;. |
Comparative FT-IR plots for neat SD and for the decontamination solutions enriched with different concentrations of nanosized adsorbents are illustrated in Figure 2. The FT-IR analysis offers valuable information about the main groups present in the structure of the components from the decontamination solutions.
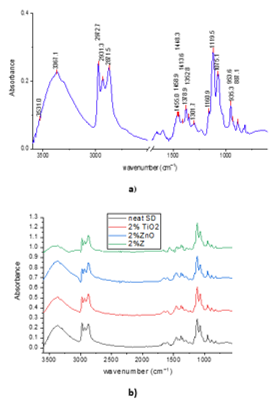 |
Fig. 2. FT-IR spectra: (A) neat SD and (B) decontamination solutions with NPs. |
Decontamination efficiency evaluated on two chemical warfare agents - mustard gas (HD) , soman (GD) and on biological warfare agent Bacillus anthracis .
The main degradation products of CWA, obtained in this study, were summarized in the schematic illustration found in Figure 3.
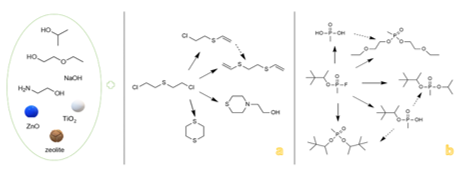 |
Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of the main degradation products of HD (a) and GD (b) obtained through the decontamination process with SD-NPs suspensions. |
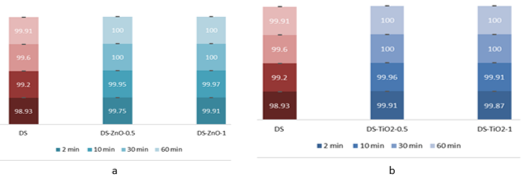
The evaluation of the decontamination efficacy of the NPs-based decontamination solutions mustard gas (HD) (Figure 4) and soman (GD) (Figure 6). The remanant toxic concentrations are summarized in Figures 5 and 7, for HD and GD, respectively.
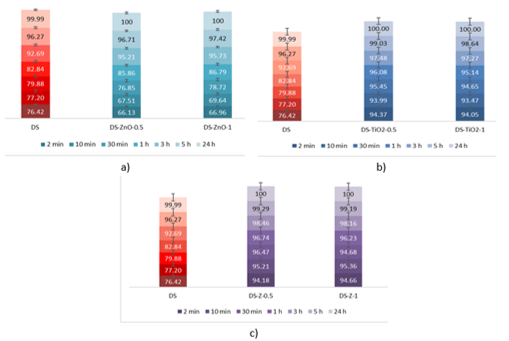 |
.Figure 4 – Decontamination degrees of sulfur mustard (HD) obtained for decontamination formulations containing: (a) ZnO, (b) TiO2 and (c) zeolite |
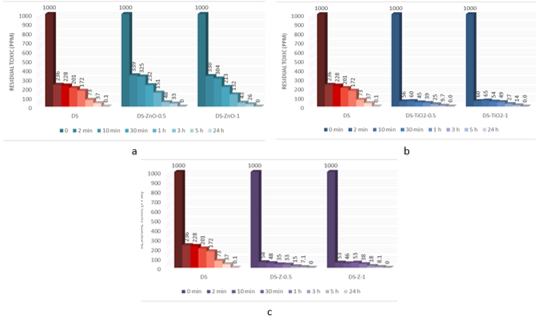 |
Figure 5 – Residual sulfur mustard after employing decontamination formulations |
 |
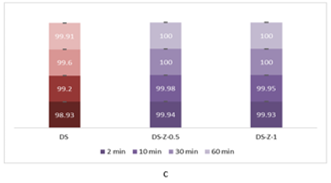 |
Figure 6 – Decontamination degrees of soman (GD) obtained for decontamination formulations containing: (a) ZnO, (b) TiO2 and (c) zeolite |
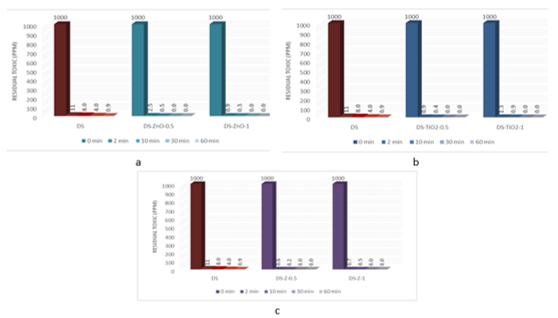 |
Figure 7 – Residual soman after employing decontamination formulations |
Dissemination
1.Reactive organic suspensions comprising ZnO, TiO2 and zeolite nanosized adsorbents: evaluation of decontamination efficiency on soman and sulfur mustard, Toxics 2021, 9, 334, https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9120334
Autors: R. Ginghina 1,‡, A. Bratu 1,‡, G. Toader2,*, A. Moldovan2,*, T. Tiganescu2, R. Oncioiu1, P. Deliu1, R. Petre1, G. Epure1, M. Purica3
2. Solution processed reduced graphene oxide thin films on glass substrate for photodection applications, 13 th - Internation Conference on Physics of Advanced Materials -ICPAM'13, September 24-30 2021, Barcelona, 24.09.2021 – 30.0. 2021, Abstract Book ICPAM 13, pp.171-172, Authors: Florin Comanescu, Cosmin Obreja, Munizer Purica
